Varicose veins
Celine HaarhoffVaricose veins are a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. They are often associated with older age but can also develop in younger individuals. While the exact cause of varicose veins is not fully understood, genetics is believed to play a role in a person's risk of developing the condition.
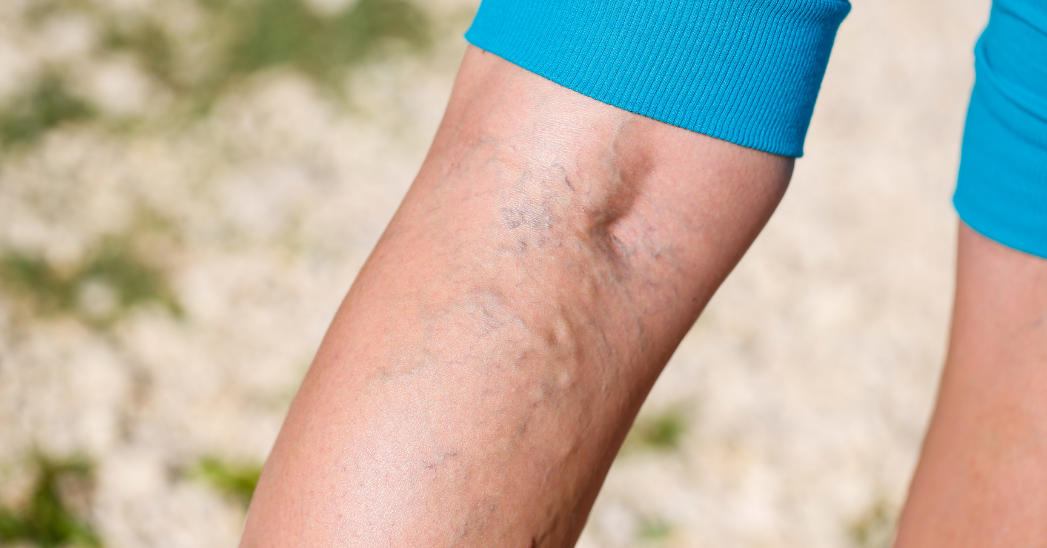
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins most often found in the legs and feet. They occur when the valves in the veins become weak or damaged, causing blood to pool in the veins and making them enlarge. This can cause the veins to become visibly swollen and twisted under the skin.
Symptoms of varicose veins can include aching or heavy feeling in the legs, swelling in the legs or ankles, and skin changes around the veins, such as redness, discoloration, or ulcers. In some cases, varicose veins can cause pain, discomfort, or cramping.
While the exact cause of varicose veins is not fully understood, genetics is believed to play a role in a person's risk of developing the condition. Certain genetic variations have been found to be associated with an increased risk of developing varicose veins.
For example, some studies have found that individuals with certain variants in the VEGF-A gene are more likely to develop varicose veins.
In addition to genetics, other factors that can increase a person's risk of developing varicose veins include:
- Older age.
- Being overweight or obese.
- Being pregnant.
- Having a family history of varicose veins.
- Standing or sitting for long periods.
A genetic test can help determine if a person has genetic variations associated with an increased risk of developing varicose veins. The test involves analyzing a sample of a person's DNA, which can be collected through a simple cheek swab. The DNA is then tested for specific genetic variations associated with an increased risk of developing varicose veins.
Suppose a person is found to have genetic variations that are associated with an increased risk of developing varicose veins. In that case, they can work with their healthcare provider to develop a plan to manage their risk.
This may include lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly, and medical treatment options, such as compression stockings or vein procedures.
Varicose veins are a common condition that can cause discomfort and other symptoms. Genetics is believed to play a role in a person's risk of developing the condition, and a genetic test can help determine if a person is at increased risk.


