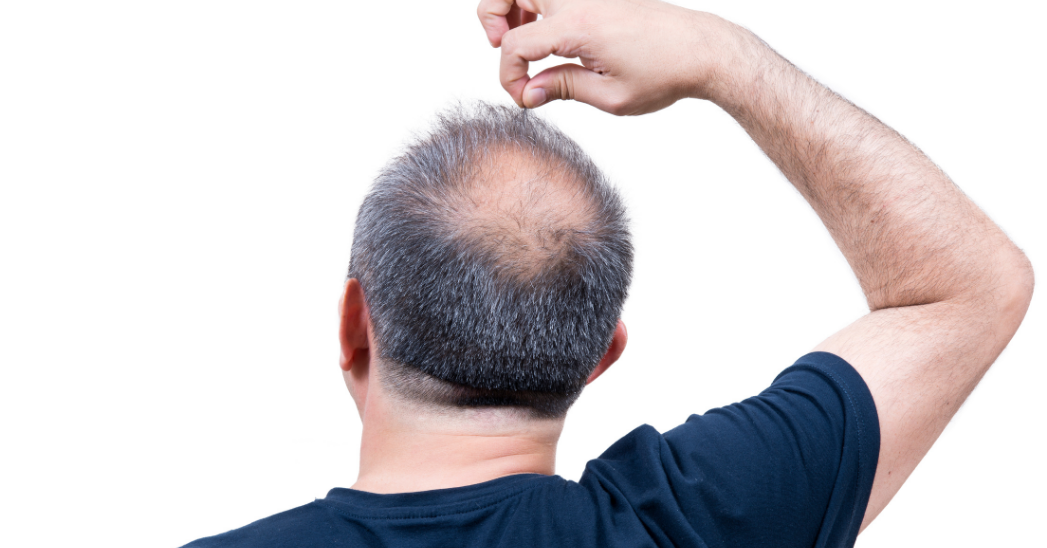
Male-pattern baldness
Celine HaarhoffBaldness, also known as alopecia, is a common condition that affects many men. While some men may experience baldness due to aging or other factors, others may be genetically predisposed to the condition.
This article will discuss the genetic factors that can contribute to male baldness, its symptoms, and how a genetic test can help determine if you are at risk for the condition.
First, let's talk about what causes male baldness. Men's most common form of baldness is androgenetic alopecia, also known as male pattern baldness. A combination of hormones and genetics causes this type of baldness.
Men with this condition have high levels of androgens, which are male hormones, in their bodies. These hormones cause the hair follicles on the scalp to shrink, resulting in thinning hair and baldness.
While the exact cause of androgenetic alopecia is not fully understood, genetics play a significant role in the development of the condition. Research has shown that male pattern baldness can be inherited from either parent. If your father or mother has male pattern baldness, you are more likely to develop the condition yourself.
So, what are the symptoms of male pattern baldness? One of the most common symptoms is a receding hairline, which is when the hairline begins to move back from the forehead. This can happen gradually or suddenly and can be one of the first signs of the condition. Another common symptom is thinning hair on the top of the head, which can occur gradually or suddenly.
In some cases, men with male pattern baldness may develop a bald spot on the top of their head, accompanied by thinning hair on the sides and back of the head.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, you must see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. Your doctor can determine if you have male pattern baldness and recommend a treatment plan. In some cases, treatment may not be necessary if the baldness is not causing any discomfort or distress. However, if the baldness is causing emotional distress or impacting your daily life, your doctor may recommend treatment options such as medication or hair transplant surgery.
One way to determine if you are at risk for male pattern baldness is to undergo a genetic test. This type of test can identify specific genes associated with the condition. If you have these genes, it does not necessarily mean that you will develop male pattern baldness, but it does increase your risk for the condition.
A genetic test for male pattern baldness is a simple and non-invasive procedure. It typically involves taking a saliva or blood sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The test results can provide valuable information about your risk for the condition and help you make informed decisions about your health and well-being.
In conclusion, male pattern baldness is a common condition caused by a combination of hormones and genetics. If you have a family history of the condition, you may be at an increased risk of developing it yourself. The symptoms of male pattern baldness include a receding hairline, thinning hair on the top of the head, and a bald spot on the top.
A genetic test can help determine if you are at risk for the condition and provide valuable information about your health. If you are experiencing symptoms of male pattern baldness, it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.


